FAQs



Hydrogen Fuel Cell System, a mechanical device, operates based on lectrochemical reactions. Unlike the engine that uses combustion, the fuel cell utilizes a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen, creating electricity, heat, and water. Fuel cells have many practical uses, from powering buildings to transportation. What makes fuel cells stand out is their cleanliness and efficiency. Unlike batteries, they do not need recharging; they keep generating electricity as long as you provide them with hydrogen. Fuel cells are reliable, silent, and have few moving parts.


The hydrogen gas is refueled at a station in a storage tank that can withstand high pressure. From the tank, the hydrogen is transferred into the fuel cell as needed, where it undergoes a reverse electrolysis process. The fuel cell comprises two plates: a negative electrode (anode) and a positive electrode (cathode), separated by an electrolyte membrane. Hydrogen (H2) is introduced at the anode, while oxygen (O2) is supplied from the ambient air to the cathode. In an electrolyte membrane, a catalyst plays a pivotal role in the electrochemical process. It facilitates the separation of hydrogen atoms into protons and electrons. Protons can pass through the electrolyte membrane, but electrons cannot. Protons are directed toward the oxygen at the cathode, where they will meet oxygen to turn into water (H2O). As electrons are compelled through the external circuit, they produce the primary source of electricity. The electric current, generated by the fuel cell stack, powers the motor that moves the wheels. The excess electric current is utilized to recharge the battery. When additional power is required during truck operations, the battery provides an extra boost, much like the workings of a BEV. A control unit manages the interplay between the fuel cells and the battery to optimize energy usage.
Fuel cells hold immense potential for revolutionizing the way we power our society. These advanced energy conversion devices offer a clean and efficient alternative to traditional methods, promising to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions while providing a reliable source of power.
Here are five benefits of utilizing fuel cells:
Zero-Emission: Hydrogen fuel cells are a clean energy solution, producing only electricity, heat, and water without harmful emissions. They contribute to sustainability goals embraced by forward-thinking companies.
Reliability: Hydrogen fuel cell technology is proven durable, performing well in extreme conditions, from -30 to 45 degrees Celsius to harsh weather and material handling warehouses, making it adaptable to various environments.
Efficiency: Hydrogen fuel cells are highly efficient, with over 60% efficiency compared to internal combustion engines' 25%. They refuel in just 3 to 20 minutes, depending on the size of the vehicle, and boost productivity.
Scalability: Fuel cell products feature modular design, enhancing reliability and ease of maintenance. Their scalability allows customization for diverse power needs, whether for vehicles, material handling fleets, or stationary power.
Lower Operational Costs: Fuel cell systems eliminate battery-related hassles, reduce labor, offer space efficiency, and lower operational costs by up to 84% compared to combustion generators.

The rapid refueling capability positions fuel cell technology as a compelling competitor in clean commercial usage. This is because commercial vehicles tend to run a fixed route, making it easier to access hydrogen for refueling. Commercial vehicles also demand a shorter downtime compared to ordinary passenger vehicles. Refueling a hydrogen fuel cell commercial vehicle takes much less time than recharging the batteries of an electric vehicle, but fuel cells create the same range and power. Hence, fuel cell trucks and buses have emerged as successful and effective applications. Furthermore, the adoption of fuel cells extends to manned aircraft and ships. Weight plays a pivotal role in the design of both aircraft and ships. Utilizing fuel cells to reduce battery weight not only enhances performance but also frees up additional space. The application also extends to non-vehicles such as houses, factories, and cranes, where hydrogen tanks can be regularly switched out to continuously generate power without the need for a huge space for batteries.

Hydrogen, the universe's most abundant element, consists of one proton and one electron. Though plentiful on Earth, it's rarely found as a free gas but often binds with other elements.
Therefore, hydrogen production involves extracting it from molecules in which it is bound. The two most commonly used methods are electrolysis and steam-methane reforming.
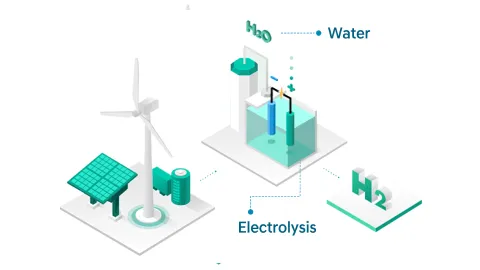
Electrolysis separates hydrogen from water (H2O) by using an electric current. Pure hydrogen and oxygen are the sole products of electrolysis, without any other byproducts or emissions. If the electricity powering this process is from renewable energy, it is labeled Green Hydrogen.

75% of global commercial hydrogen is produced via steam-methane reforming (SMR). In this process, steam (1,300°F to 1,800°F) reacts with methane at pressure (3-25 bar), yielding primarily hydrogen. The primary source of methane is natural gas.
Other methods of hydrogen production include thermochemical processes that transform biomass into gases or liquids to extract the hydrogen, photolytic methods that utilize solar power to break water into its hydrogen and oxygen component, and biological techniques that involves using organisms like bacteria and microalgae to generate hydrogen through natural reactions.
Apart from the previous active productions, there exists a type known as by-product hydrogen, which means hydrogen is collected as a side product of petrochemical processes. It offers the benefit of being economically efficient, as it doesn't necessitate extra investment in infrastructure for its production.
There are still several obstacles to tackle before we fully embrace a hydrogen society.
Pricing Challenges: Renewable hydrogen production costs are much higher than their fossil counterparts. It needs to achieve economies of scale to reduce the consumer price.
Lack of Infrastructure: Tapping into renewable resources from distant sites necessitates infrastructure investments, everything from pipelines to storage solutions.
Differentiation Issues: Currently, there's no standardized method to distinguish low-carbon hydrogen from its fossil-based counterpart. This absence results in challenges to creating incentives for production, and leaving consumers uninformed about the source and environmental footprint of the hydrogen they consume.
Absence of Hydrogen Market: Since hydrogen isn't traded as a commodity yet, it lacks a price index. This lack of transparency and competition can elevate costs for consumers.
However, various efforts are being made to overcome these challenges. In 2023, the EU planned to allocate up to €471 billion ($500 billion) in advancing CO2-free renewable energy sourced hydrogen. Concurrently, in 2023, the U.S. Department of Energy unveiled a $47.7 million allocation for 16 hydrogen technology research and development initiatives, emphasizing cost reduction and infrastructure enhancement.

Renewable energy derives from natural resources that are self-sustainable and able to replenish themselves at a rate exceeding their utilization.
These natural sources are abundant and found all over the world.
In order for natural resources to be considered sources of renewable energy, they must meet two requirements.
First, these resources should exist naturally and be consistently available. Second, they must possess
the ability to replenish themselves over time without causing significant pollution or environmental harm.
Widely known renewable energy sources are wind, water, and sunlight, which have coexisted with humanity throughout history
It is worth noting that the accessibility of renewable energy depends on factors such as location, time, and weather conditions. Nevertheless, the production and utilization of renewable energy continue to grow due to its immense potential to generate essential power, including electricity, heating, and transportation fuels.
There are six well-defined categories of renewable energy sources that can be harnessed for various applications:

Solar Energy: The earth receives an astounding amount of sunlight within just 90 minutes, which is enough to meet the global energy demands for an entire year. It is worth noting that over 173,000 terawatts of solar energy continually reach our planet, surpassing global energy consumption by over 10,000 times. Technologies like photovoltaic panels (commonly referred to as solar panels) and concentrating solar-thermal power (CSP) systems are used to capture sunlight and convert it into solar energy.

Wind Energy: Wind is everywhere on Earth’s surface. This renewable energy source operates by utilizing the kinetic energy transmitted by moving air to rotate generators and produce electricity. While average wind speeds differ depending on location, the technical potential of wind energy surpasses global electricity production. It can produce around 60 million kWh every year.

Hydropower Energy: Hydropower draws upon the movement of water from higher to lower elevations to generate energy. There are two types of hydropower: river hydropower and reservoir hydropower. The river hydropower plants capture the energy from flowing rivers, and the reservoir hydropower plants use stored water in reservoirs for energy production. Currently, hydropower stands as the largest renewable source for electricity generation.

Ocean Energy: Also known as tidal energy, ocean energy is created from the kinetic and thermal energy of ocean waves and currents to generate electricity or heat. Ocean energy has the potential to surpass current global energy demands.

Geothermal Energy: Geothermal energy comes from the utilization of thermal energy from the earth's interior. Heat sourced from geothermal reservoirs, including those deep underground, is collected and processed to generate renewable energy. Hydrothermal reservoirs, which are naturally hot and permeable, have been in operation for over a century and are widely regarded as dependable sources of geothermal energy.

Bioenergy: Also known as biomass energy, bioenergy is generated from a diverse range of organic materials, such as wood, manure, and agricultural crops, which can be transformed into power and heat. Even though the usage of bioenergy causes emissions of greenhouse gases, it produces lower levels of greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, making it a relatively cleaner energy source.
Moving away from fossil fuels, which not only deplete but can also pollute the environment, renewable energy sources present numerous advantages that go beyond just power generation. These are some of the benefits of utilizing renewable energy:
Environmental Advantages: During operation, renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydropower have little to zero environmental impact due to their zero emissions. Renewable energy can slow down climate change-induced calamities.
Abundance and Infinitude: Renewable energy comes from sources that are either plentiful or infinite, and they are easy to access compared to finite fossil fuels.
Energy Autonomy Renewable energy guarantees energy freedom, both at the individual and national levels. Households equipped with solar panels or wind turbines can generate their own electricity, diminishing their reliance on centralized energy providers. Additionally, at national levels, countries can use a mix of different energy sources to stop relying on other countries for energy sources.
Economic Advancement and Job Creation: The renewable energy sector has grown and contributed to economic expansion and job proliferation. Investments in renewable energy infrastructure create new industries and employment opportunities.
Diminished Operational Expenses: Once the initial infrastructure investments are realized, the ongoing expenses, including fuel, upkeep, and maintenance, can be reduced.
Technological Progression: Improvements in technology continue to enhance efficiency and enable us to tap into the full potential of natural energy sources, leading to technological progress.
Enhanced Air Quality and Public Health: The utilization of renewable energy generally contributes to the reduction of pollution, which leads to fewer health issues, which can also diminish healthcare expenditures.
Global Collaboration: The adoption of renewable energy fosters international cooperation and synergy. Renewable energy initiatives frequently entail partnerships and accords that promote global sustainability.